how health affects the family.
* * * f a m i l y * * *
Family dynamics significantly impact health in both positive and negative ways.
Having a close-knit and supportive family provides emotional support, economic well-being, and increases overall health. However, the opposite is also true. When family life is characterized by stress and conflict, the health of family members tend to be negatively affected.
Positive Aspects of Family Dynamics and Health
Negative Aspects of Family Dynamics and Health
Problematic and non-supportive familial interactions have a negative impact on health. “There is increasing evidence that poor-quality relationships can actually harm physical and mental health. Indeed, persons in unhappy marriages exhibit worse physical and mental health than unmarried persons.”
Further, marriages characterized by an unequal division of decision making and power are associated with high levels of depression on the part of both spouses.
Growing up in an unsupported, neglectful or violent home is also associated with poor physical health and development.
Family Dynamics and Children
Families characterized by conflict, anger, and aggression have particularly negative effects on children. Physical abuse and neglect represent immediate threats to the health of children.
In addition, “the fact that children’s developing physiological and neuroendocrine systems must repeatedly adapt to the threatening and stressful circumstances created by these environments increases the likelihood of biological dysregulations that may contribute to a buildup of allostatic load, that is, the premature physiological aging of the organism that enhances vulnerability to chronic disease and to early mortality in adulthood.”
Children who grow up in risky families are also especially likely to exhibit risky behaviors such as smoking, alcohol abuse, and drug abuse. “Anger and aggression are highly noxious agents in a family environment. Conditions ranging from living with irritable and quarreling parents to being exposed to violence and abuse at home show associations with mental and physical health problems in childhood, with lasting effects in the adult years.”
Children as Caretakers
Family can also have a negative impact on children if the illness of a parent or family member results in a child taking on the role of a caretaker. When a child acts as a caretaker, s/he often misses school and oftentimes must assume the personal and domestic responsibilities that his/her parents are no longer able to complete.
A national survey estimates that 1.3 to 1.4 million young people aged 8 to 18 years serve as family caregivers to ill or disabled family members. Some child caregivers do everything adult family caregivers do, including administering injections and medications, which they are often untrained to do.
Though families frequently have no other choice but to have a child serve as a caretaker, putting a child in this role may jeopardize their educational, social, and emotional development.
Having a close-knit and supportive family provides emotional support, economic well-being, and increases overall health. However, the opposite is also true. When family life is characterized by stress and conflict, the health of family members tend to be negatively affected.
Positive Aspects of Family Dynamics and Health
- A family's social support is one of the main ways that family positively impact health. Social relationships, such as those found in close families, have been demonstrated to: decrease the likelihood of the onset of chronic disease, disability, mental illness, and death.
- Marriage is thought to protect well-being by providing companionship, emotional support, and economic security; is associated with physical health, psychological well-being, and low mortality.
- One study found that “controlling or taking into account every other risk factor for death that we know, including physical health status and rates of all-cause mortality are twice as high among the unmarried as the married.”
- Another study found that “on the whole, marriage produces a net improvement in avoiding the onset of disease, which is called primary prevention.”
- Married people are more likely to avoid risky behavior, such as heavy drinking and high fat diets, and married people are also more likely to see the doctor for checkups and screenings.
- One does not have to be married. social support from parents, friends, and relatives have positive effects, especially on mental health.
- Social integration and social support, like marriage, have protective effects on reducing mortality risks. For example, “those reporting higher levels of support from close friends and family exhibit lower heart rate and systolic blood pressure, lower serum cholesterol, and higher immune function.”
- Thus, available data provide evidence to support the idea that one’s social environment or family situation “does get under the skin to affect important physiologic parameters, including neuroendocrine, immune, and cardiovascular functioning.”
Negative Aspects of Family Dynamics and Health
Problematic and non-supportive familial interactions have a negative impact on health. “There is increasing evidence that poor-quality relationships can actually harm physical and mental health. Indeed, persons in unhappy marriages exhibit worse physical and mental health than unmarried persons.”
Further, marriages characterized by an unequal division of decision making and power are associated with high levels of depression on the part of both spouses.
Growing up in an unsupported, neglectful or violent home is also associated with poor physical health and development.
Family Dynamics and Children
Families characterized by conflict, anger, and aggression have particularly negative effects on children. Physical abuse and neglect represent immediate threats to the health of children.
In addition, “the fact that children’s developing physiological and neuroendocrine systems must repeatedly adapt to the threatening and stressful circumstances created by these environments increases the likelihood of biological dysregulations that may contribute to a buildup of allostatic load, that is, the premature physiological aging of the organism that enhances vulnerability to chronic disease and to early mortality in adulthood.”
Children who grow up in risky families are also especially likely to exhibit risky behaviors such as smoking, alcohol abuse, and drug abuse. “Anger and aggression are highly noxious agents in a family environment. Conditions ranging from living with irritable and quarreling parents to being exposed to violence and abuse at home show associations with mental and physical health problems in childhood, with lasting effects in the adult years.”
Children as Caretakers
Family can also have a negative impact on children if the illness of a parent or family member results in a child taking on the role of a caretaker. When a child acts as a caretaker, s/he often misses school and oftentimes must assume the personal and domestic responsibilities that his/her parents are no longer able to complete.
A national survey estimates that 1.3 to 1.4 million young people aged 8 to 18 years serve as family caregivers to ill or disabled family members. Some child caregivers do everything adult family caregivers do, including administering injections and medications, which they are often untrained to do.
Though families frequently have no other choice but to have a child serve as a caretaker, putting a child in this role may jeopardize their educational, social, and emotional development.
how health affects the country.
* * * C o u n t r y * * *
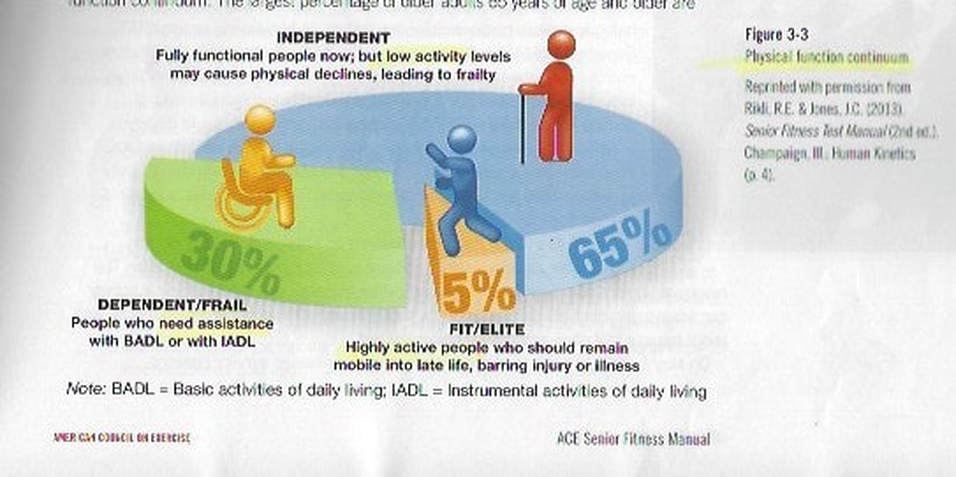
Physical function continuum
are you part of the 65%?
where will you be 10 to 20 years from now?
will you be a caregiver or need a caregiver?
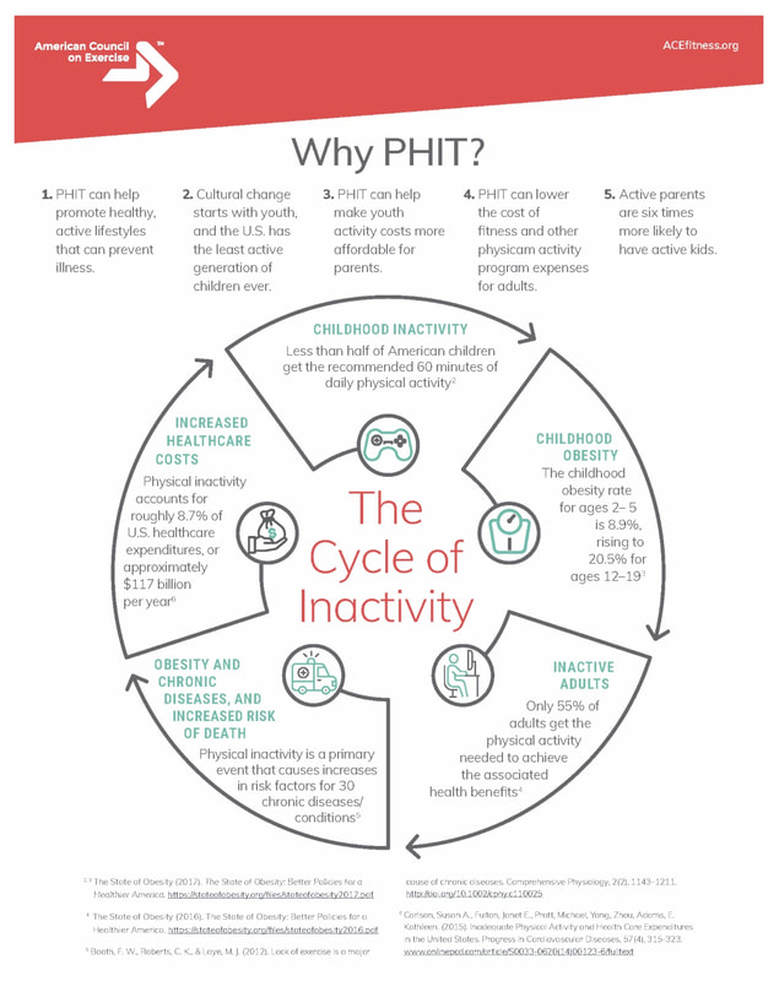
obesity trends in the U.S.
the state of adult obesity
The US obesity prevalence was 41.9% in 2017 – March 2020.
From 1999 –2000 through 2017 –March 2020, US obesity prevalence increased from 30.5% to 41.9%.
During the same time, the prevalence of severe obesity increased from 4.7% to 9.2%. Obesity-related conditions include heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes and certain types of cancer.
These are among the leading causes of preventable, premature death. The estimated annual medical cost of obesity in the United States was nearly $173 billion in 2019 dollars.
Medical costs for adults who had obesity were $1,861 higher than medical costs for people with healthy weight.
the state of Childhood obesity
Childhood obesity is a serious problem in the United States, putting children and adolescents at risk for poor health. Obesity prevalence among children and adolescents is still too high.
For children and adolescents aged 2-19 years in 2017-20201: The prevalence of obesity was 19.7% and affected about 14.7 million children and adolescents. Obesity prevalence was 12.7% among 2- to 5-year-olds, 20.7% among 6- to 11-year-olds, and 22.2% among 12- to 19-year-olds. Childhood obesity is also more common among certain populations.
* * * * * * * * *
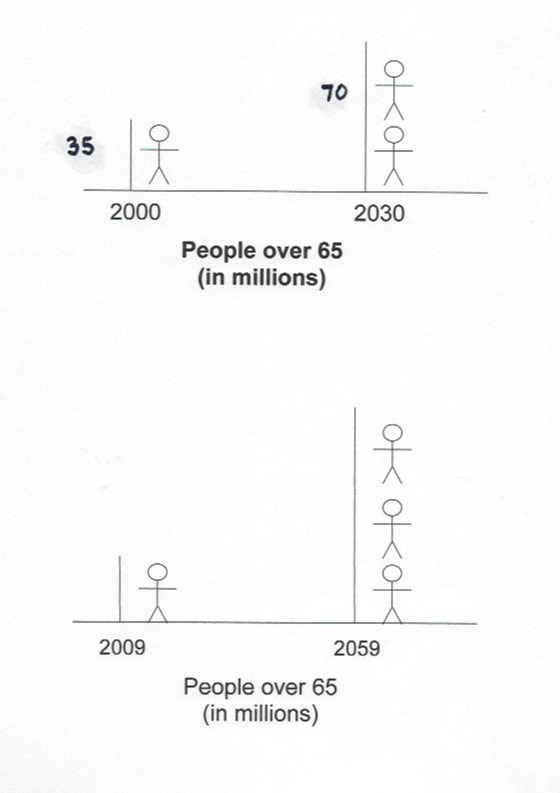
projected populations
predictions: over 65 populations double in 30 yrs. &
triple in 50 Yrs.
scary stuff...
Note: as a visual learner, i developed these infographics to help me understand my studies
with american council on excercise (ace).
Then, i figured if it helped me it might help others realize
the importance of health and physical activity.
with american council on excercise (ace).
Then, i figured if it helped me it might help others realize
the importance of health and physical activity.
*****
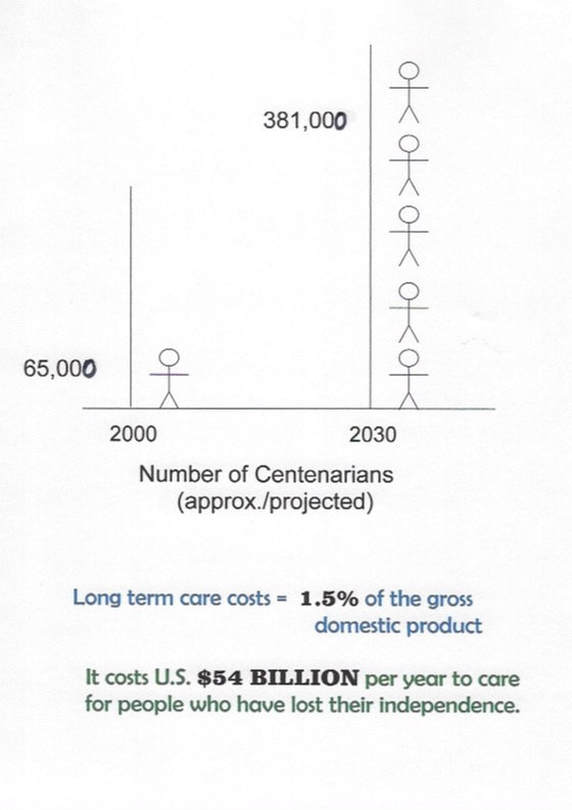
number of centenarians predicted to multiply by 5 in 30 yrs.
how health affects the world.